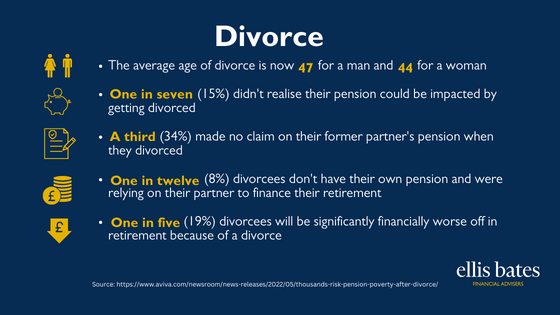
Divorce and my Pension
https://www.ellisbates.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Pensions-and-Divorce-560-×-315px.png 560 315 Jess Easby Jess Easby https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/70f816837c455030814d46a740cfc12d89893aaf8cbf8c8f8f59387d7b30ac08?s=96&d=mm&r=g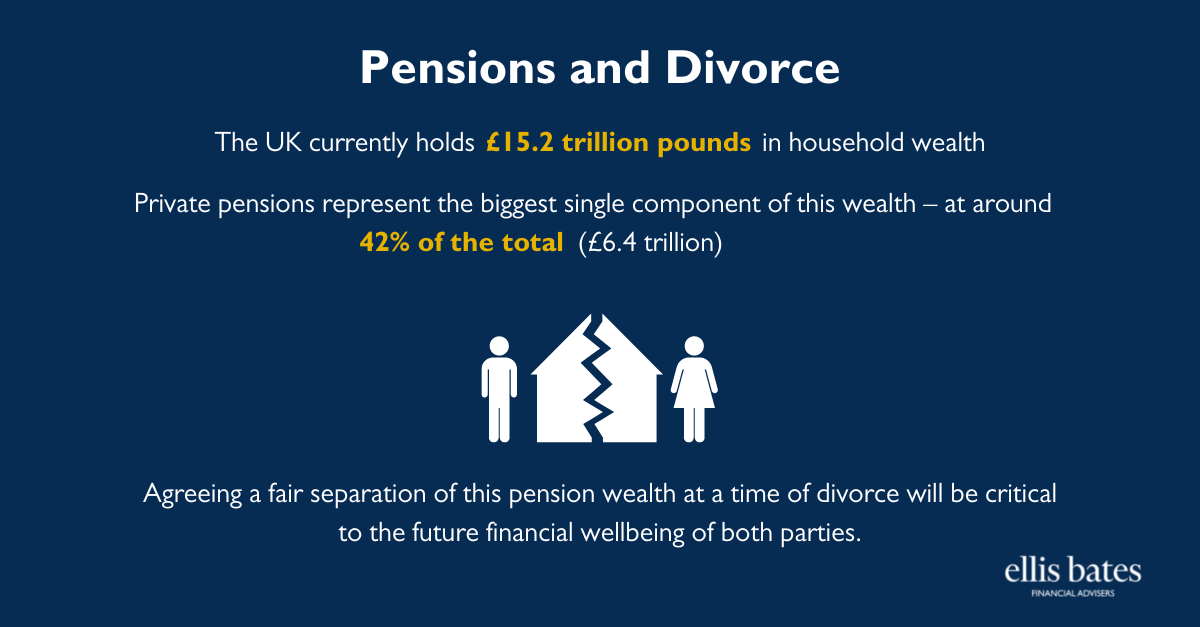
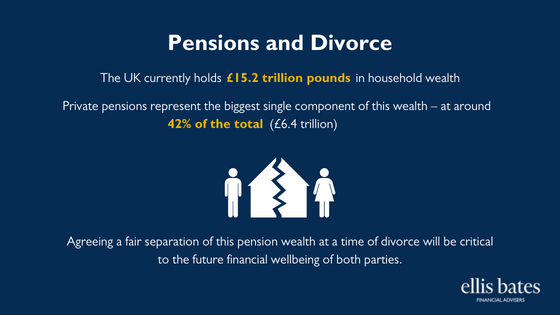
- The UK currently holds £15.2 trillion pounds in household wealth
- Private pensions represent the biggest single component of this wealth – at around 42% of the total (£6.4 trillion)
- Agreeing a fair separation of this pension wealth at a time of divorce will be critical to the future financial wellbeing of both parties
If you’re going through a divorce and would like to discuss your options regarding your pensions then please contact us.