Free Guide: Enhancing Pension Contributions
https://www.ellisbates.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Ebookbrochure-socials-8-1-1024x535.png 1024 535 Jess Easby Jess Easby https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/70f816837c455030814d46a740cfc12d89893aaf8cbf8c8f8f59387d7b30ac08?s=96&d=mm&r=gPlanning for your retirement is one of the most important financial decisions you will make and no matter what your age or how far away from retirement you are, putting savings plans in place as early as possible to maximise your pension pot is vital.
We have produced a free Guide to Enhancing Pension Contributions for a Brighter Future to help you decide how to maximise your pension savings :






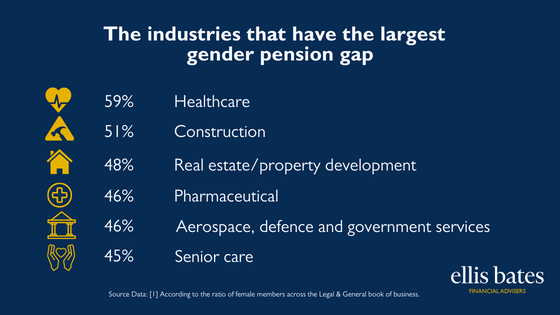

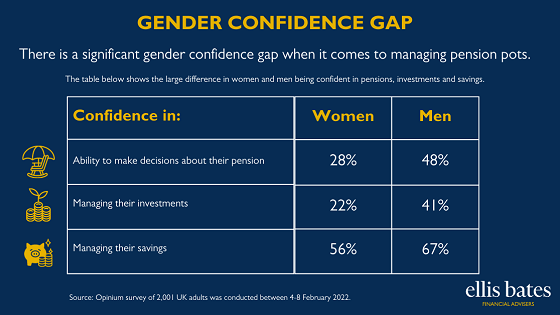
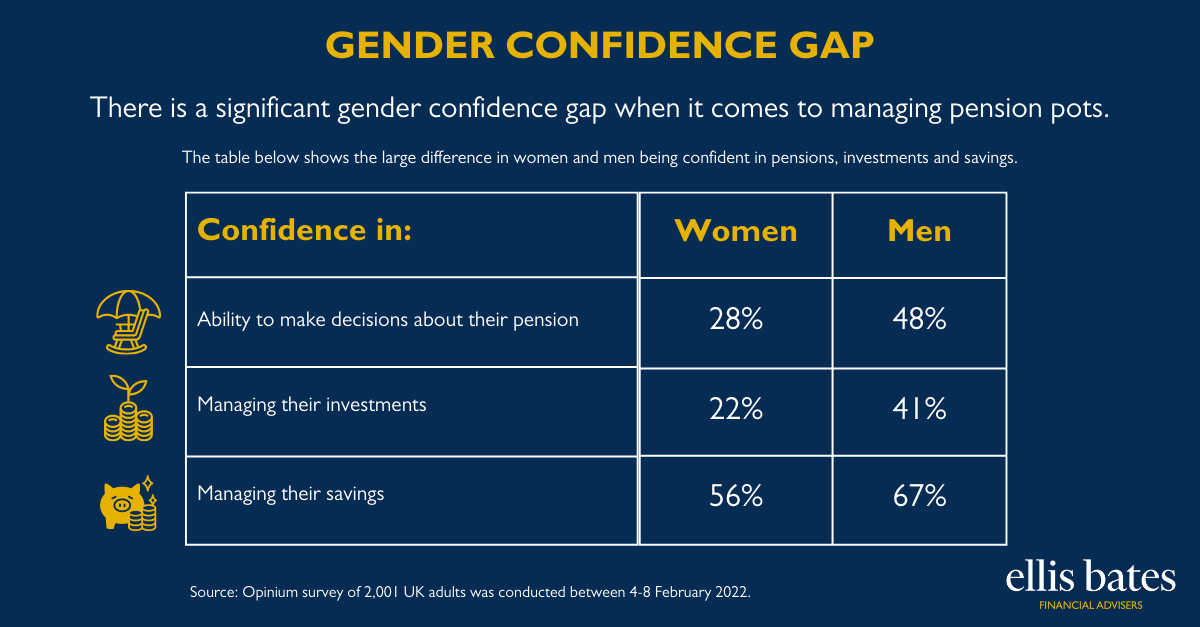


 Women are being urged to think about their long term savings
Women are being urged to think about their long term savings