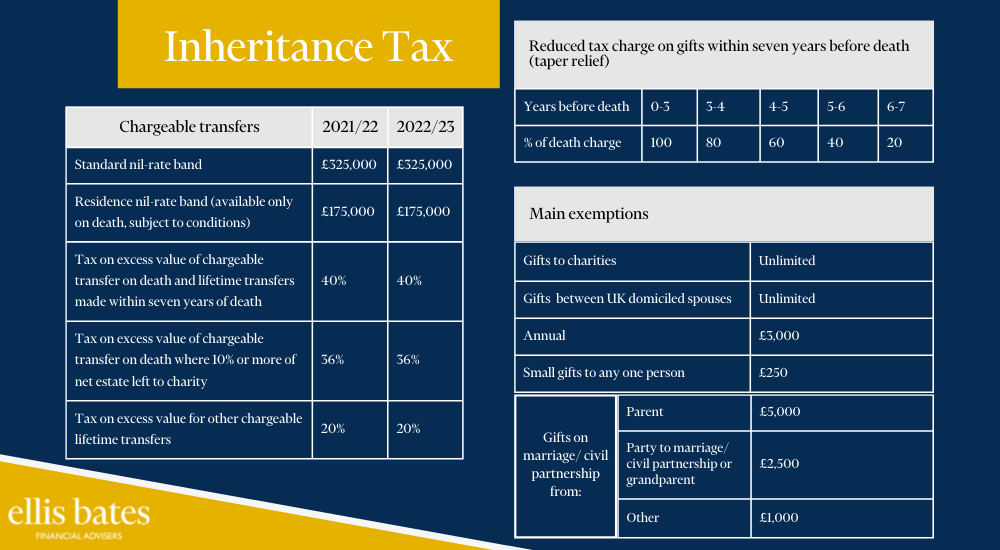
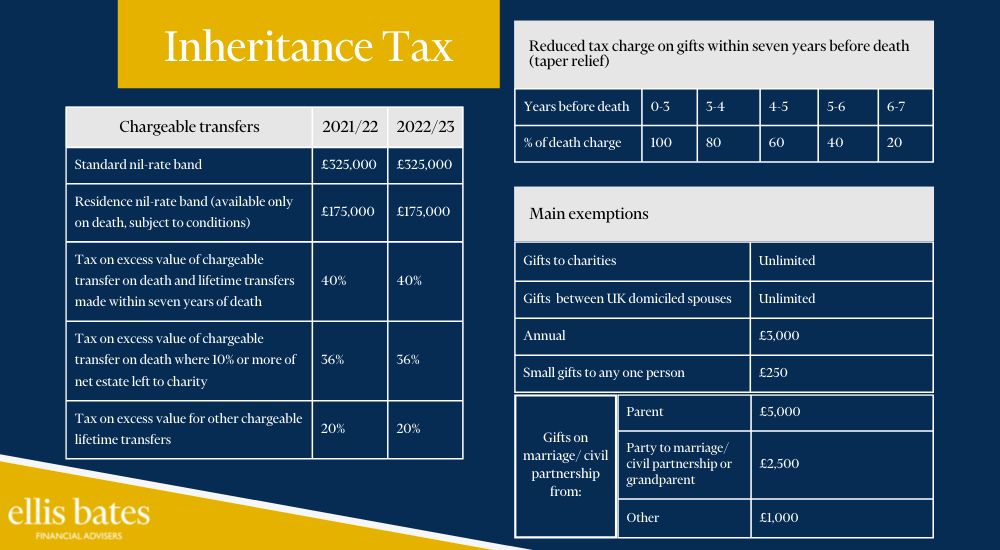
What are the thresholds for Inheritance Tax
https://www.ellisbates.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Inheritance-Tax-blog-graphic-1.png 1000 550 Jess Easby Jess Easby https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/70f816837c455030814d46a740cfc12d89893aaf8cbf8c8f8f59387d7b30ac08?s=96&d=mm&r=gYour estate is comprised of everything you own but one thing is for certain – you cannot take it with you when you die.
When the inevitable happens, you may want to make sure that as much of your estate reaches your heirs, rather than being depleted by tax beforehand. Rising house prices and a recovering economy means tens of thousands more families will be hit with Inheritance Tax bills, making it essential to plan ahead.
Get in touch with us to discuss your Inheritance Tax planning options.




 Time to review your financial plans with a financial check-up?
Time to review your financial plans with a financial check-up? 
 Planning your future has arguably never been more important.
Planning your future has arguably never been more important.
 Make full use of your relevant tax planning opportunities
Make full use of your relevant tax planning opportunities
 How to create a personal financial plan in 8 steps
How to create a personal financial plan in 8 steps
 Are you scared of running out of money in retirement?
Are you scared of running out of money in retirement?
 Discovering the emotional benefits of financial advice!
Discovering the emotional benefits of financial advice!